how is surfactant administered to premature babies
Surfactant has traditionally been administered through an endotracheal tube either as bolus in smaller aliquots 21 or by infusion through an adaptor port on the proximal end of the. Some babies however particularly premature babies are born without surfactant and this causes rds.

Aarc Clinical Practice Guideline Surfactant Replacement Therapy 2013 Respiratory Care
It has become established as a standard part of the management of such.
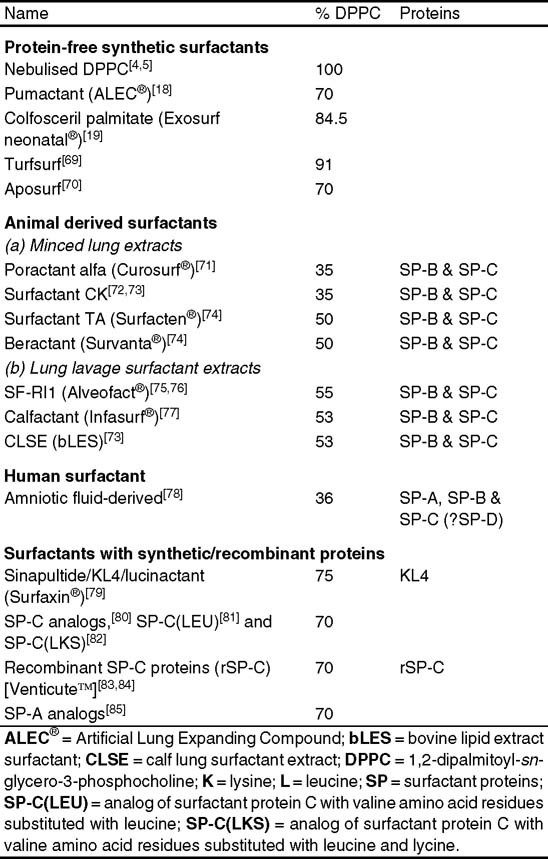
. It is used to replace the natural surfactant produced by babies lungs which is missing in. This liquid makes it possible for babies to breathe. How is surfactant administered to premature babies.
Surfactant is a kind of foamy fatty liquid that acts like. To evaluate the initial doses of surfactant administered to preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome RDS requiring surfactant therapy have been traditionally receiving surfactant by intubation surfactant and extubation technique.
This is a retrospective cohort study of 206. Surfactant is a liquid given through the breathing tube. Exogenous surfactant therapy has been a significant advance in the management of preterm infants with RDS.
It then spreads out into the air sacs of the lungs. To investigate how often surfactant was administered in preterm infants with a gestational age below 34 weeks treated with early nCPAP as a first approach to respiratory. The lungs absorb surfactant over a.
They have used six surfactant preparations. Apr 13 2022 Natural surfactant is produced by the fetus before they are born and their lungs are prepared to. Blood samples are collected through a heel stick or a needle inserted into a vein to monitor a number of critical substances including calcium glucose and bilirubin levels in your.
1 systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials confirmed that surfactant administration in preterm infants with established respiratory. The endotracheal instillation of surfactant is the most widely accepted technique. How is surfactant administered.
Surfactant is a liquid made by the lungs that keeps the airways alveoli open. The total dose is usually given less than a minute. Surfactant is administered in liquid form via an endotracheal tube in a single bolus dose as.
Surfactant replacement therapy for premature babies acts to keep the alveoli from sticking together and is supplemented with oxygen or ventilation to help the baby breathe. How often is it given. Surfactant comes in a liquid form that is squirted directly into the breathing tube.
The surfactant is administered via a thin catheter into the trachea in small aliquots while the baby is spontaneously breathing on CPAP support. How surfactant works. RDS occurs when there is not enough surfactant in the lungs.
The baby is monitored while giving surfactant. A substance called surfactant is an essential part of the process allowing alveoli to remain open.
Impact Of Surfactant Administration Through A Thin Catheter In The Delivery Room A Quality Control Chart Analysis Coupled With A Propensity Score Matched Cohort Study In Preterm Infants Plos One
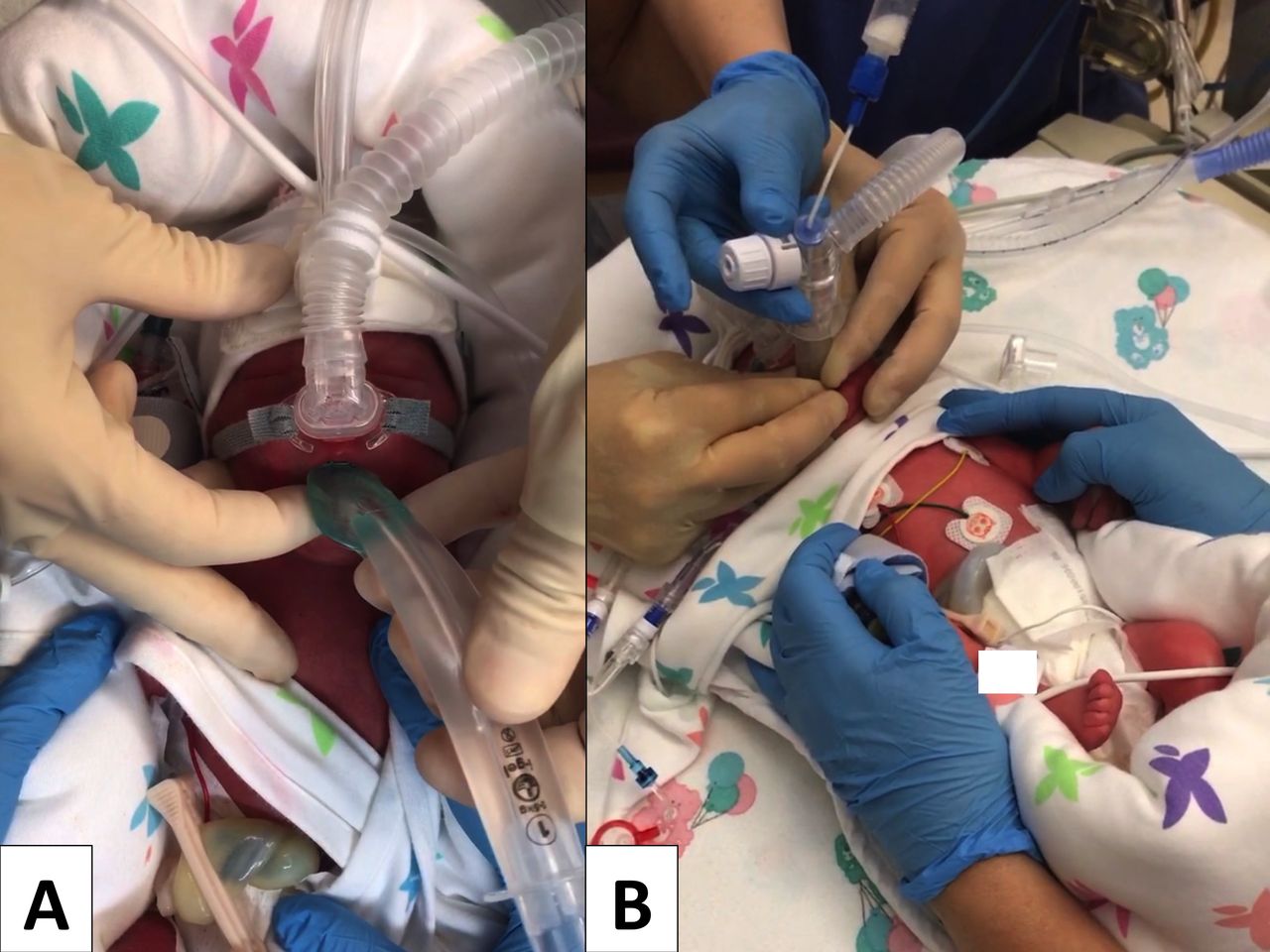
Supraglottic Airway Devices For Administration Of Surfactant To Newborn Infants With Respiratory Distress Syndrome A Narrative Review Adc Fetal Neonatal Edition
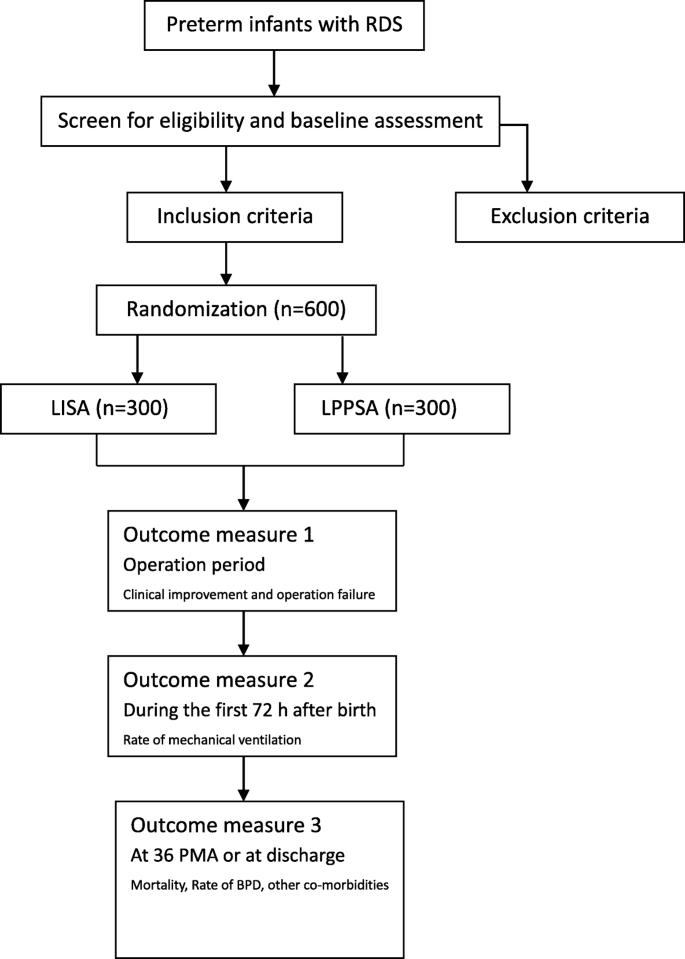
Less Invasive Surfactant Administration Versus Endotracheal Surfactant Instillation Followed By Limited Peak Pressure Ventilation In Preterm Infants With Respiratory Distress Syndrome In China Study Protocol For A Randomized Controlled Trial Trials

Bovine Surfactant Replacement Therapy In Neonates Of Less Than 32 Weeks Gestation A Multicenter Controlled Trial Of Prophylaxis Versus Early Treatment In China A Pilot Study Sciencedirect
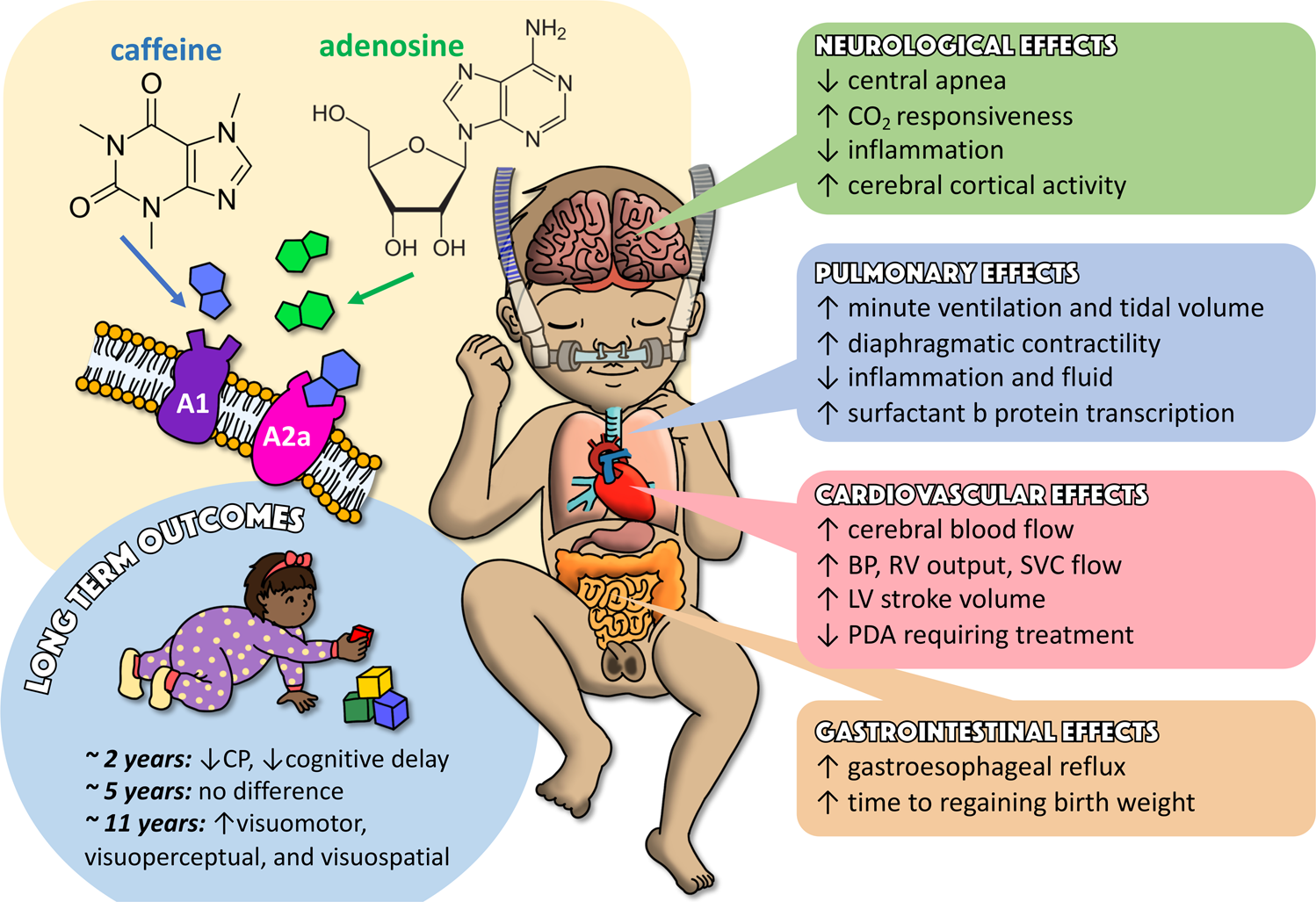
Optimizing Respiratory Management In Preterm Infants A Review Of Adjuvant Pharmacotherapies Journal Of Perinatology

Pulmonary Surfactant Medication Wikipedia

Comparison Of The Effect Of Surfactant Administration During Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure With That Of Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Alone On Complications Of Respiratory Distress Syndrome A Randomized Controlled Study
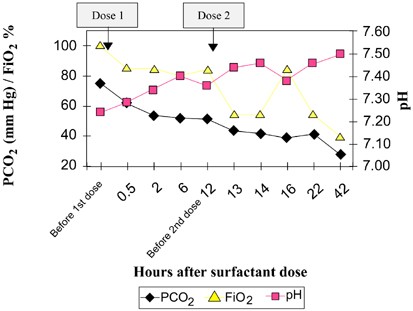
Secondary Surfactant Deficiency In Neonates Journal Of Perinatology

Less Invasive Surfactant Administration Lisa Chances And Limitations Adc Fetal Neonatal Edition
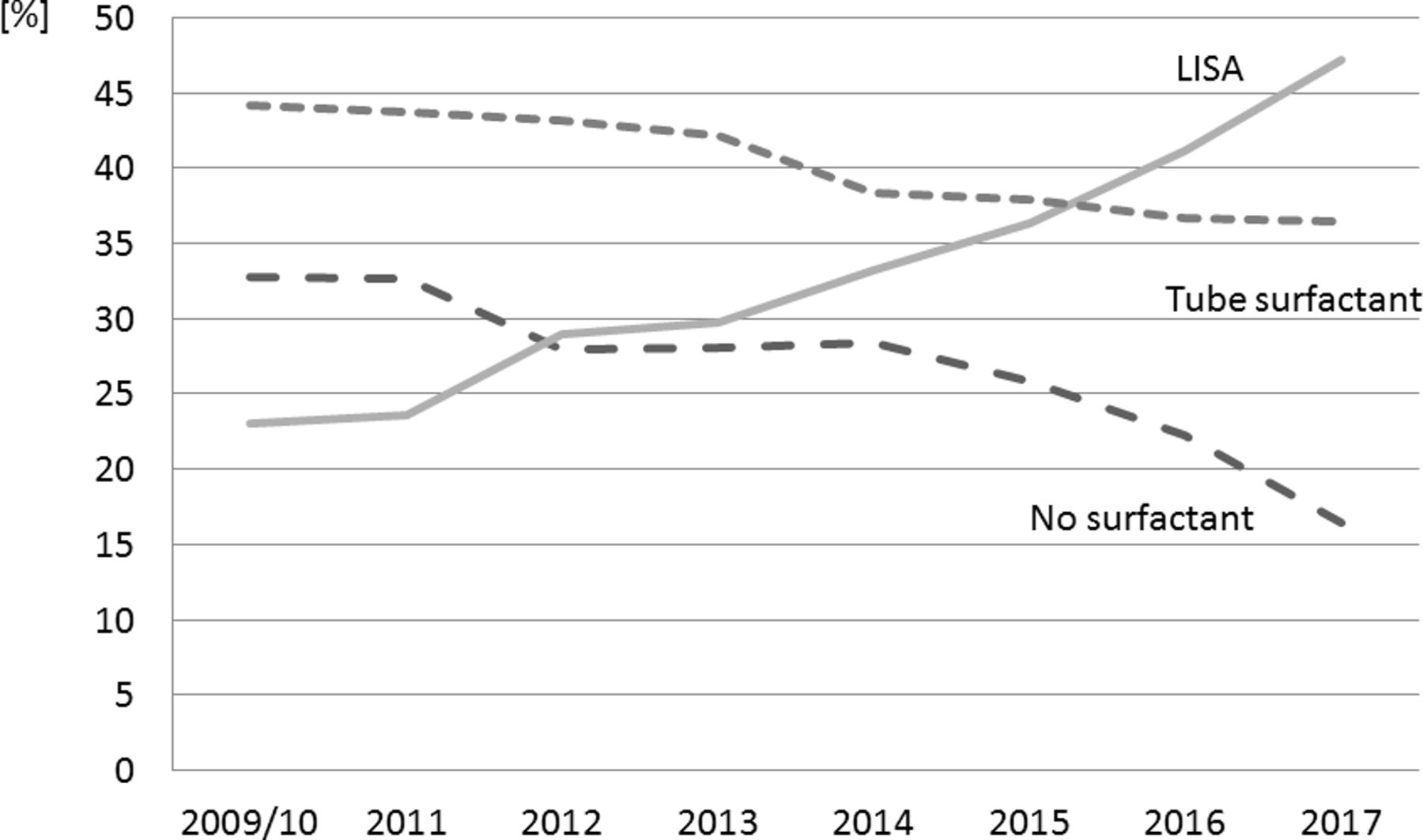
Less Invasive Surfactant Administration Lisa Chances And Limitations Adc Fetal Neonatal Edition

Less Invasive Surfactant Administration Reduces The Need For Mechanical Ventilation In Preterm Infants A Meta Analysis Christine S M Lau Ronald S Chamberlain Shyan Sun 2017

Respiratory Distress Syndrome Of The Newborn Rt
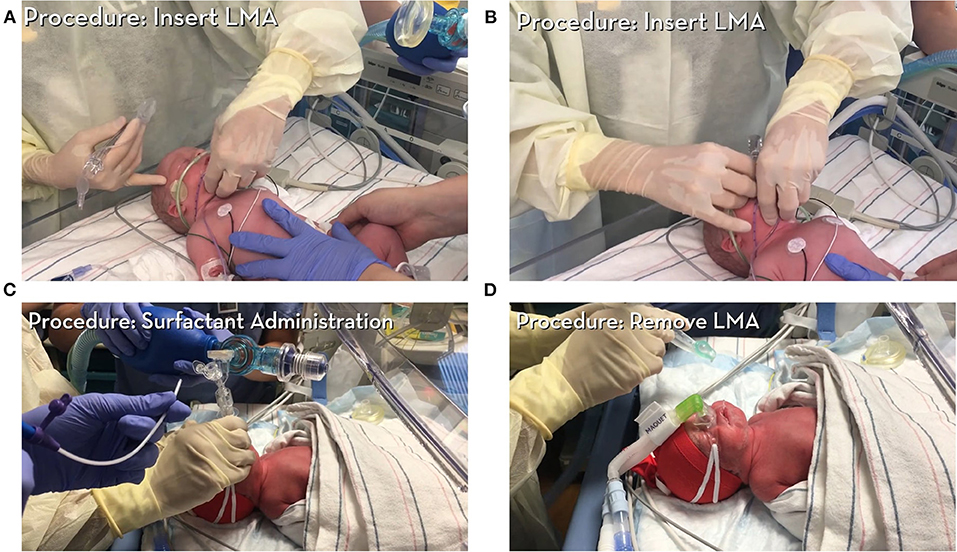
Frontiers Surfactant Administration Through Laryngeal Or Supraglottic Airways Salsa A Viable Method For Low Income And Middle Income Countries
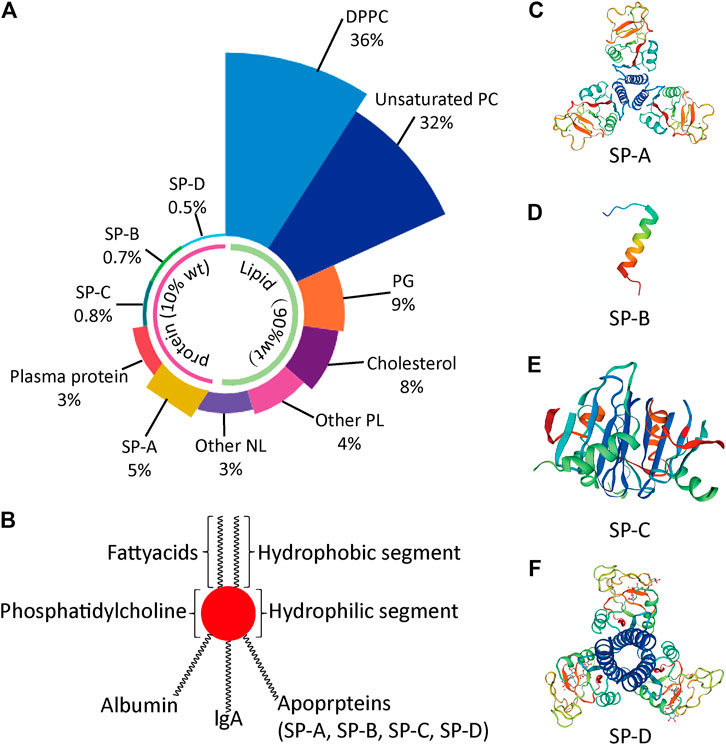
Frontiers The Role Of Pulmonary Surfactants In The Treatment Of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome In Covid 19
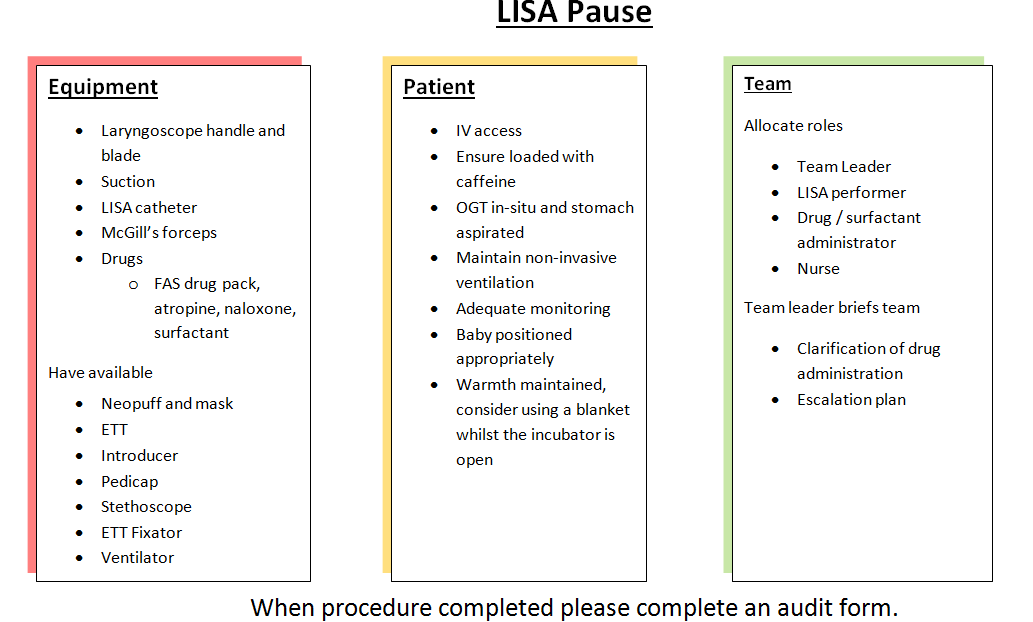
Less Invasive Surfactant Administration Lisa Neonatal Guideline

Curosurf Poractant Alfa Resources And Support Curosurf

Less Invasive Surfactant Administration A Word Of Caution The Lancet Child Adolescent Health

Minimally Invasive Surfactant Administration For The Treatment Of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome A Multicenter Randomized Study In China Abstract Europe Pmc
